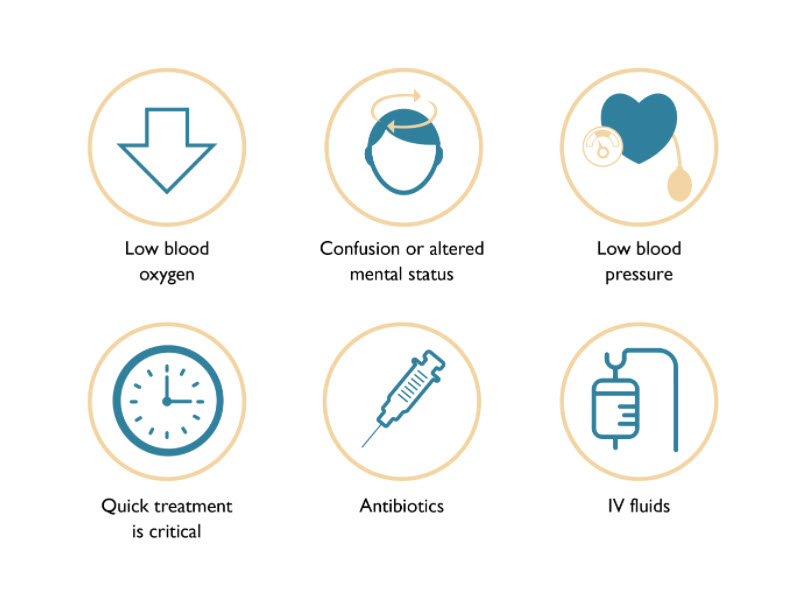
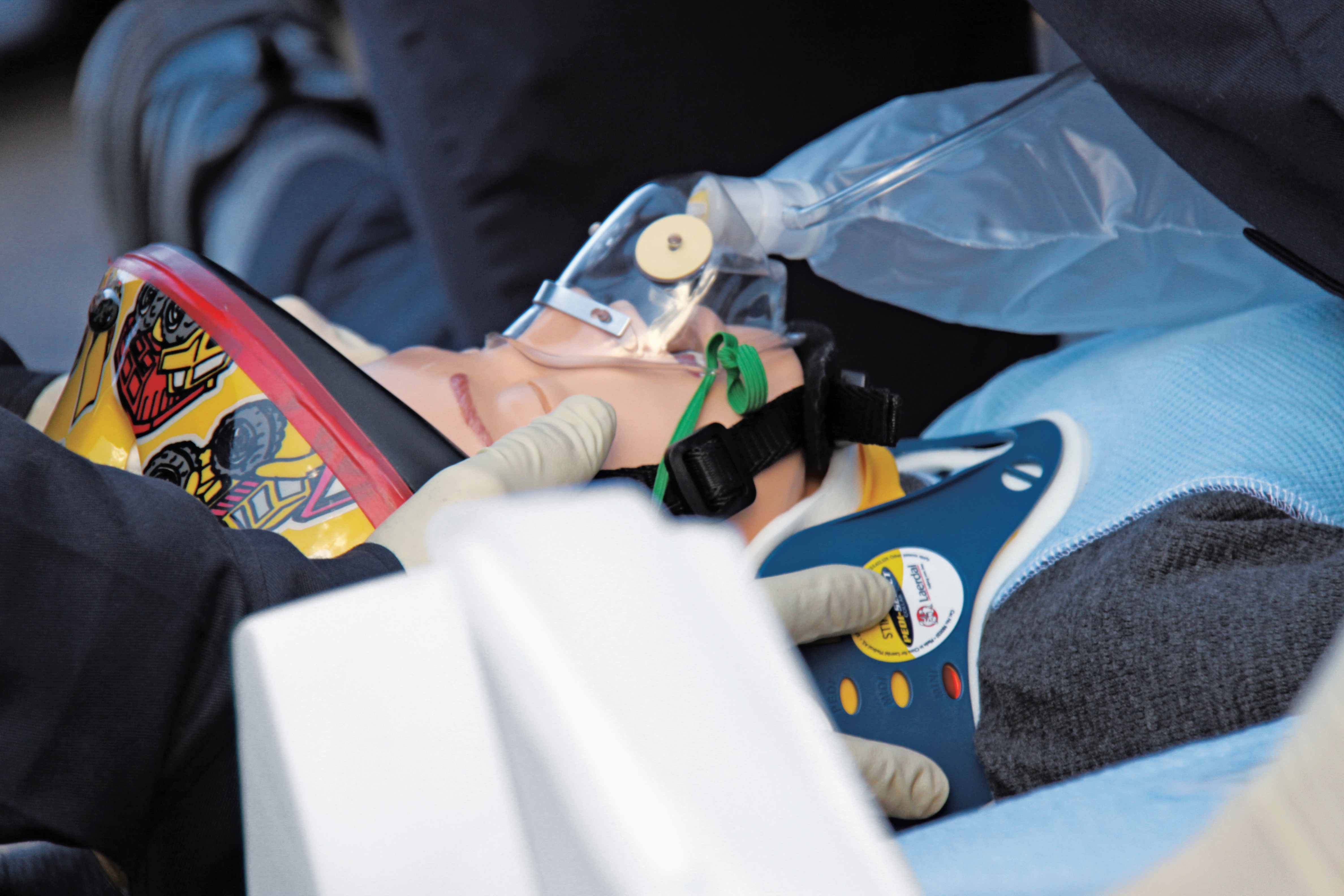
Often when healthcare professionals are provided with training, it is conducted in silos and sorted by discipline. But, cross-functional team training can positively impact a team's interactions during a high-stress, time-sensitive emergency case like severe sepsis.
Simulation can help members from different care teams, who play different roles, develop effective communication skills. With better communication and precautionary team behaviors in place, patients are more likely to receive safe care.
Dr. Arthur Childs at Cape Regional Medical Center located in the United States credits simulation for the hospital’s decrease in the number of patients with septicemia or severe sepsis.6 Prior to his team’s training with a simulator, 72% of the hospital's sepsis patients led to major complications or comorbidities. After simulation training, that percentage lowered to 63% - a result suggesting that patients with sepsis are now identified earlier.7