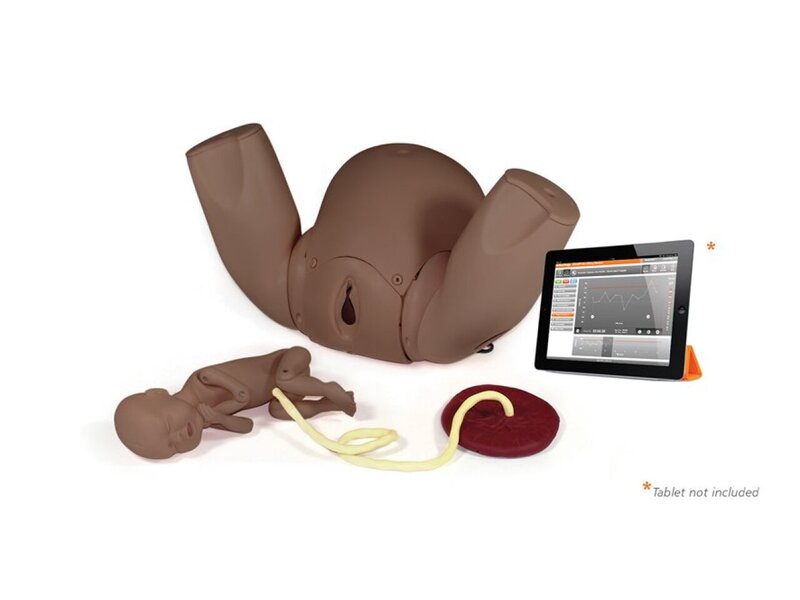
PROMPT Flex Geburtssimulator Advanced (dunkelhäutig)
Simulator - Advanced
- Dieses Produkt kann nicht online erworben werden
- Weitere Informationen anfordern
Melden Sie sich an, um dieses Element zu Ihrer Favoritenliste hinzuzufügen.
Produktinformationen
- Bluetooth enabled baby for force monitoring during shoulder dystocia drills
- Free, downloadable Birthing Simulator software allows trainees' actions and interventions to be recorded during drills, with time to deliver baby
- PDFs of trainee drills can be saved and printed for debriefing
- Software compatible with Windows, PC, iOS and Android devices
- Software scenarios can be modified or created from scratch to fit with your own language and procedures
- Suitable for use with Simulated/Standardized Patient
- Realistic pelvic floor
- Articulating thighs for McRobert’s procedure
- Stretchable perineum
- Soft, flexible birthing canal
- Additional modules available to extend training:
- Post Partum Hemorrhage management
- C-section
- Cervical Dilatation and Effacement
- Optional lower legs for all fours position
- Supports bench top training or hybrid simulation
- Skin washable with soap and water
- Latex free
- Birth canal and cervix
- Ischial spines and pubic bone
- Gynaecoid pelvis
- Articulating thighs
- Fully articulated baby with clavicles, fontanelles, flexible head, detachable umbilical cord and placenta
- Training and practice in the following types of birth:
- Normal
- Vaginal breech
- Shoulder dystocia with force feedback*
- Vaginal assisted (forceps and vacuum devices)
- Third stage of labor
- Cord prolapse
- Urinary catheter placement
- IM injection
- Communication and teamwork skills
*Force feedback is unique to this model and not available on the PROMPT Flex Standard
EVIDENCETraining for Shoulder Dystocia: A Trial of Simulation Using Low-Fidelity and High-Fidelity Mannequins.
Crofts, J. F., C. Bartlett, et al. (2006). "Training for Shoulder Dystocia: A Trial of Simulation Using Low-Fidelity and High-Fidelity Mannequins." Obstet Gynecol 108(6): 1477-1485.
Management of Shoulder Dystocia: Skill Retention 6 and 12 Months After Training.
Crofts, J. F., C. Bartlett, et al. (2007). "Management of Shoulder Dystocia: Skill Retention 6 and 12 Months After Training." Obstet Gynecol 110(5): 1069-1074.
Shoulder dystocia training using a new birth training mannequin.
Crofts, J. F. A., Georgios; Read, Mike; Sibanda, Thabani; Draycott, Timothy J. (2005). "Shoulder dystocia training using a new birth training mannequin." BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics & Gynaecology 112(7): 997-999.
Patient-actor perception of care: a comparison of obstetric emergency training using manikins and patient-actors.
Crofts, J. F. B., C; Ellis, D; Winter, C; Donald, F; Hunt, L P; Draycott, T J (2008). "Patient-actor perception of care: a comparison of obstetric emergency training using manikins and patient-actors." Quality & Safety in Health Care 17(1): 20-24.
Draycott, T. J., J. F. Crofts, et al. (2008). "Improving Neonatal Outcome Through Practical Shoulder Dystocia Training." Obstet Gynecol 112(1): 14-20.
Shoulder Dystocia: Using Simulation to Train Providers and Teams.
Fahey, J. O. M., MPH, CNM; Mighty, Hugh E. MD (2008). "Shoulder Dystocia: Using Simulation to Train Providers and Teams." Journal of Perinatal & Neonatal Nursing 22(2): 114-122.