3 Tips fi Use Simulation fi Build an Assess Competence in EMS Providers
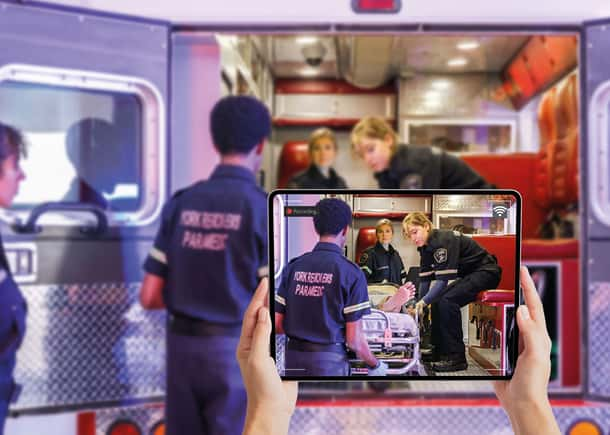


Whether yuh getting students ready for their first patient encounter or helping experienced providers sharpen their skills, one thing always the same: competence ain't built by just talk. It's earned through hands-on, realistic, and data-informed practice — and that's where simulation shines.
Simulation offers a special chance to replicate the complexity, unpredictability, and emotional intensity of real-world prehospital care. It not only builds psychomotor skills, but also develops the judgment, adaptability, and confidence that providers need to perform under pressure.
Even more importantly, it creates a structured environment for assessment: educators can evaluate performance objectively, give targeted feedback, and verify competency over time.
In this article, we explore three impactful ways to use simulation to build and assess essential competencies — from soft skills to CPR to community births — in your pre-hospital training program.
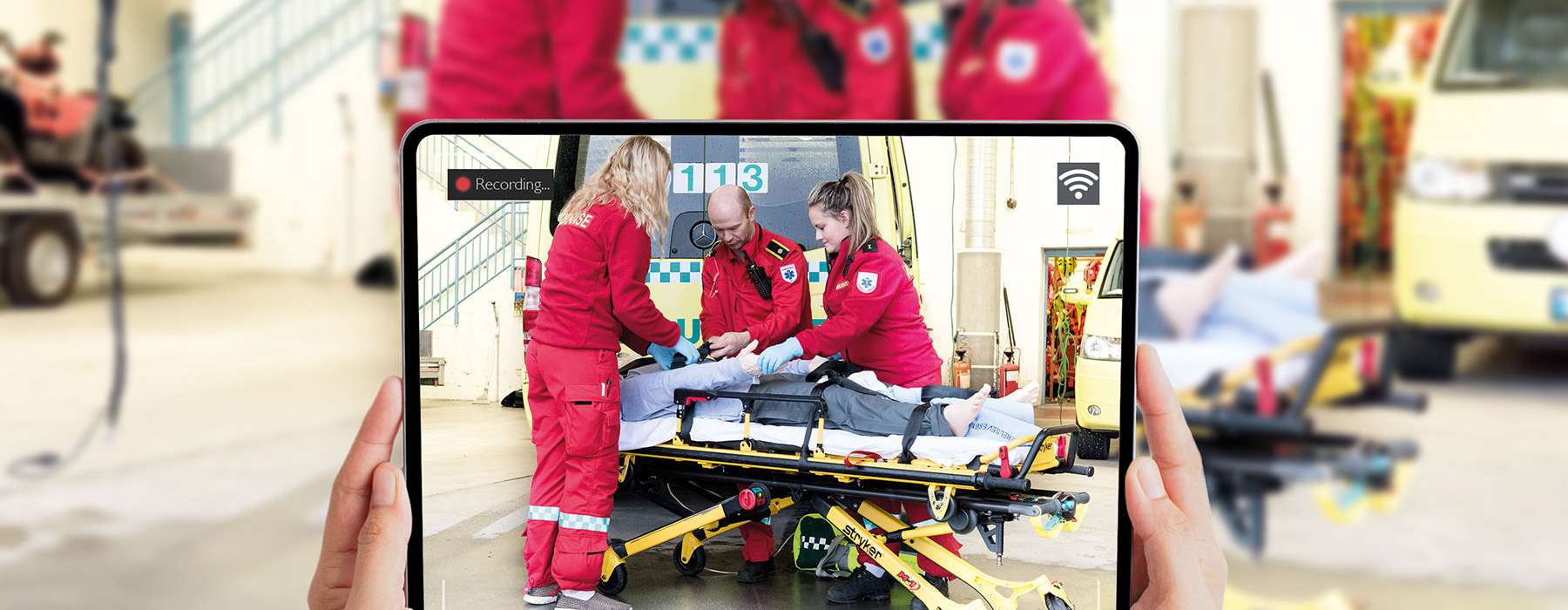

Soft skills — such as communication, teamwork, resilience, adaptability, and clinical reasoning — are some of the most challenging to learn but often distinguish a good rescuer in crisis situations from an exceptional one.
These skills come in handy when rescuers face unexpected challenges: a troublesome patient, malfunctioning equipment, or limited resources on site. They also affect how rescuers communicate with patients and their families, coordinate care with colleagues, and make decisions under pressure.
How to teach and assess soft skills using simulations:
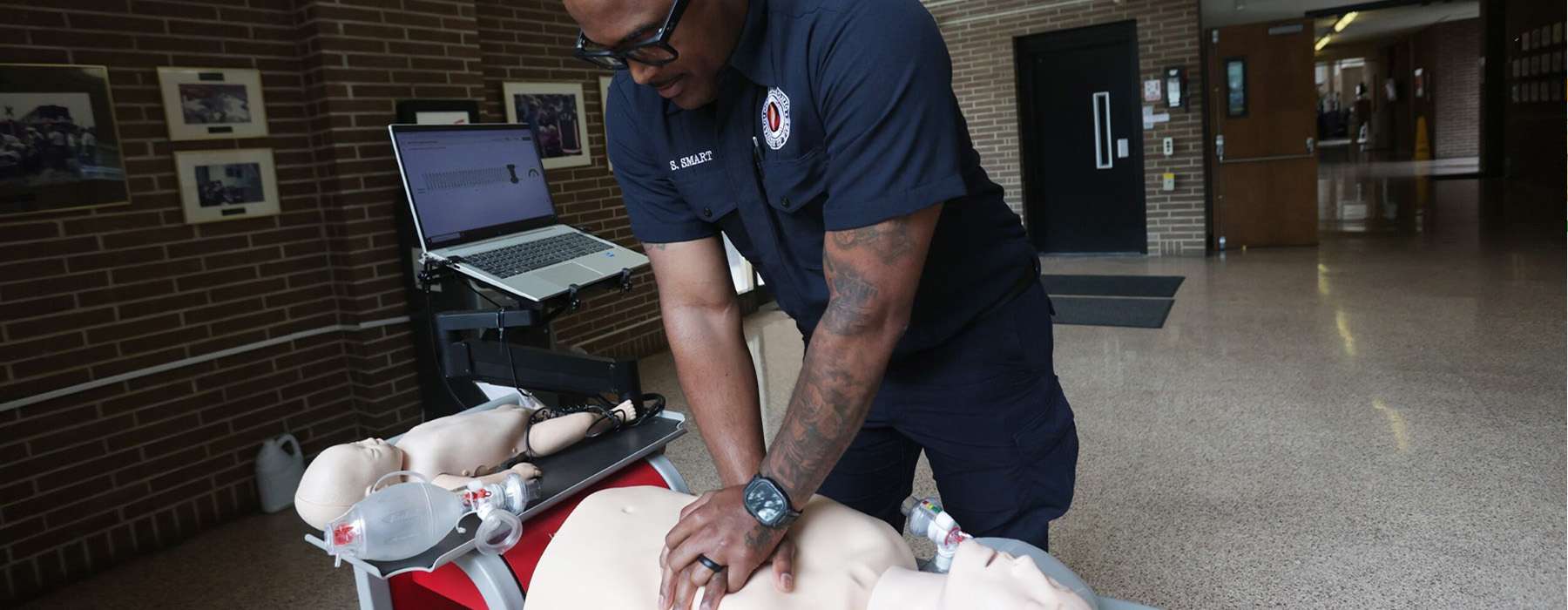
CPR is one of the most fundamental — and most fleeting — skills in emergency care. While many healthcare providers initially master chest compressions and ventilations during certification, competence often declines without regular and targeted practice.
Traditional skills refresher courses, typically conducted once or twice a year, are not enough to maintain high quality performance.Research shows that training with low doses and high frequency — shorter, more frequent practice sessions — is more effective for skill retention and performance.
How to teach and assess resuscitation with simulation:
Assessment tip: Optimal CPR simulation tools provide real-time feedback and performance data that can be stored, analyzed, and used to verify competence for both initial certification and ongoing education.
Programs like Resuscitation Quality Improvement® (RQI®) and HeartCode® Complete offer scenario-based CPR training paired with objective performance feedback.
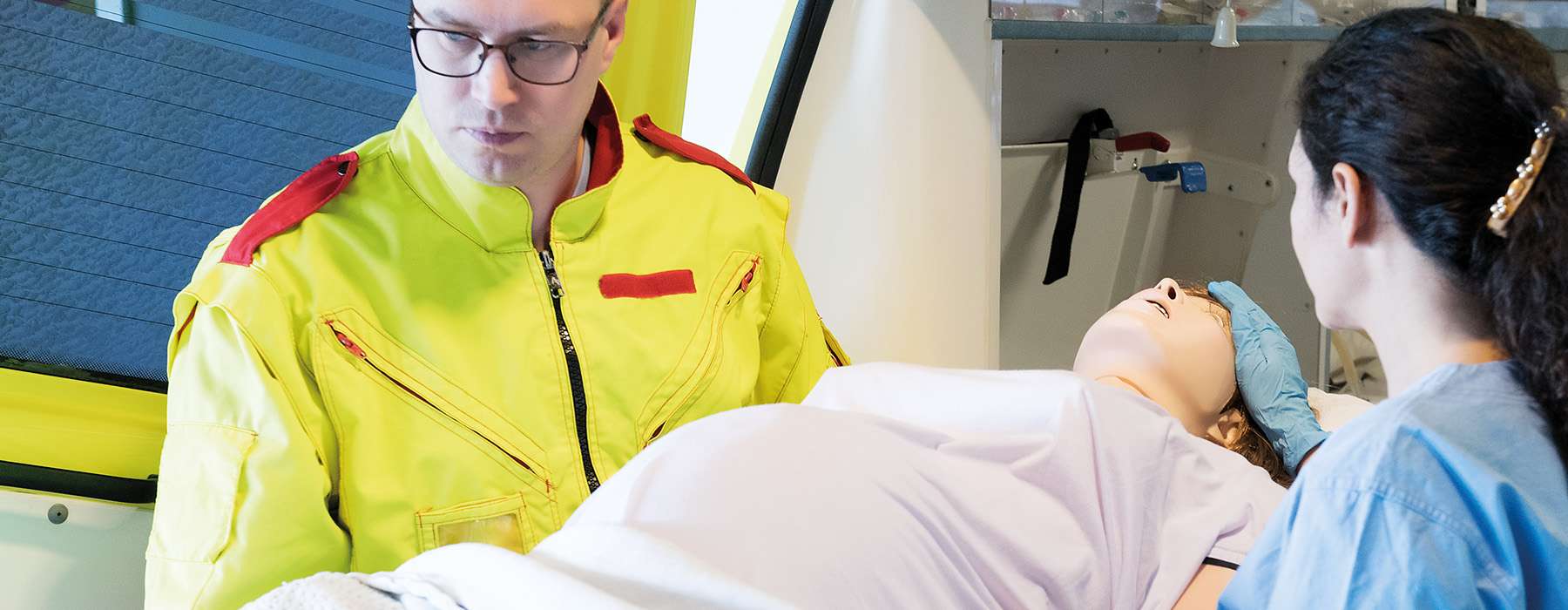

Few situations test the calm and clinical skills of a pre-hospital care worker like an unexpected birth outside the hospital. These calls require quick assessment, clear communication, and safe execution of skills that many caregivers rarely get the chance to practice.
Simulation offers a safe way to prepare students for the full spectrum of obstetric emergencies—from uncomplicated births to shoulder dystocia and postpartum hemorrhage.
How to Teach and Assess Obstetric Competence Using Simulation:
Assessment Tip: During training for obstetric emergencies, document not only procedures but also decision-making ability and communication under pressure.