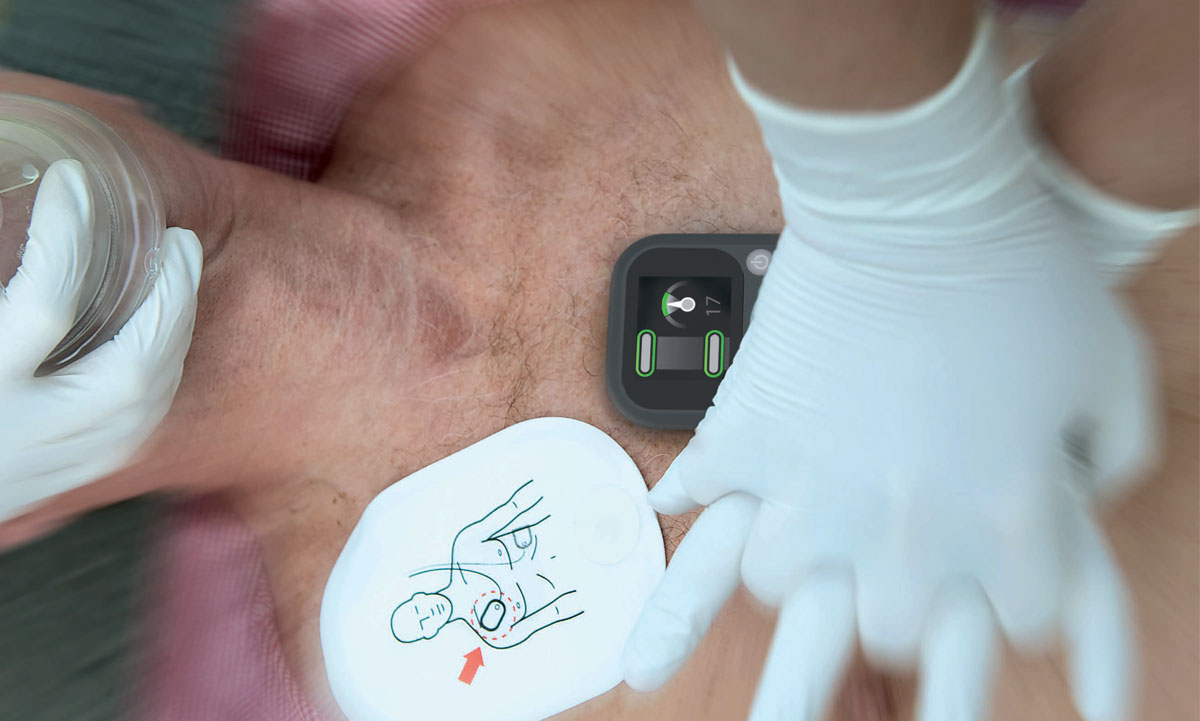
Measure to Improve
Help ensure quality CPR with real-time feedback.
Medicine has traditionally relied on a “see one, do one” approach to learning and experience. Didactic learning in this context focuses on imparting knowledge. Simulation-based learning makes that knowledge come alive in a setting designed to mimic real clinical encounters and lifelike experiences. In this environment, clinicians can refine their individual and team skills well before touching a real patient.
Learners and providers who use simulation experience a higher level of engagement and show greater personal involvement in their training. Additionally, simulation has been shown to increase retention rates and has been associated with a higher rate of learning transfer to the job.
In this article, we highlight ways in which leaders in healthcare are using simulation to: