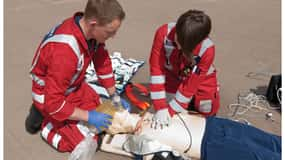
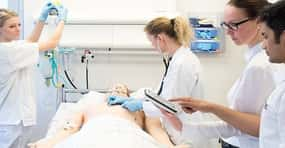
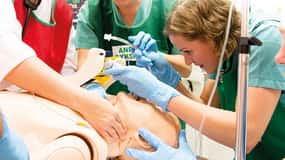
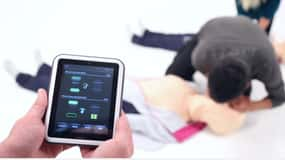
Facilitated debriefing
Facilitated debriefing is a way to take the lessons of an event and create a structured plan for self-improvement. Facilitator-led feedback includes discussion of events, reflection, and assimilation of activities enable long-term learning. Feedback about performance can be received from an instructor, a peer, or a computer either during or after the simulation.