Preparing Practice-Ready Physicians
With the anticipated global shortage of 11 million health workers by 2030 (WHO,2024) the need to produce practice-ready graduates in all fields of healthcare has reached critical levels.
Enhancing Medical Training through CBME and EPAs
Competency-Based Medical Education (CBME) is a framework that focuses on outcomes, emphasizing the abilities of healthcare professionals to perform tasks in real-world settings.
Entrustable Professional Activities (EPAs) are the cornerstone of assessment for medical school in CBME (AAMC, 2022). They define the critical tasks that learners must be able to perform independently and reliably as a measure of their readiness for unsupervised practice.
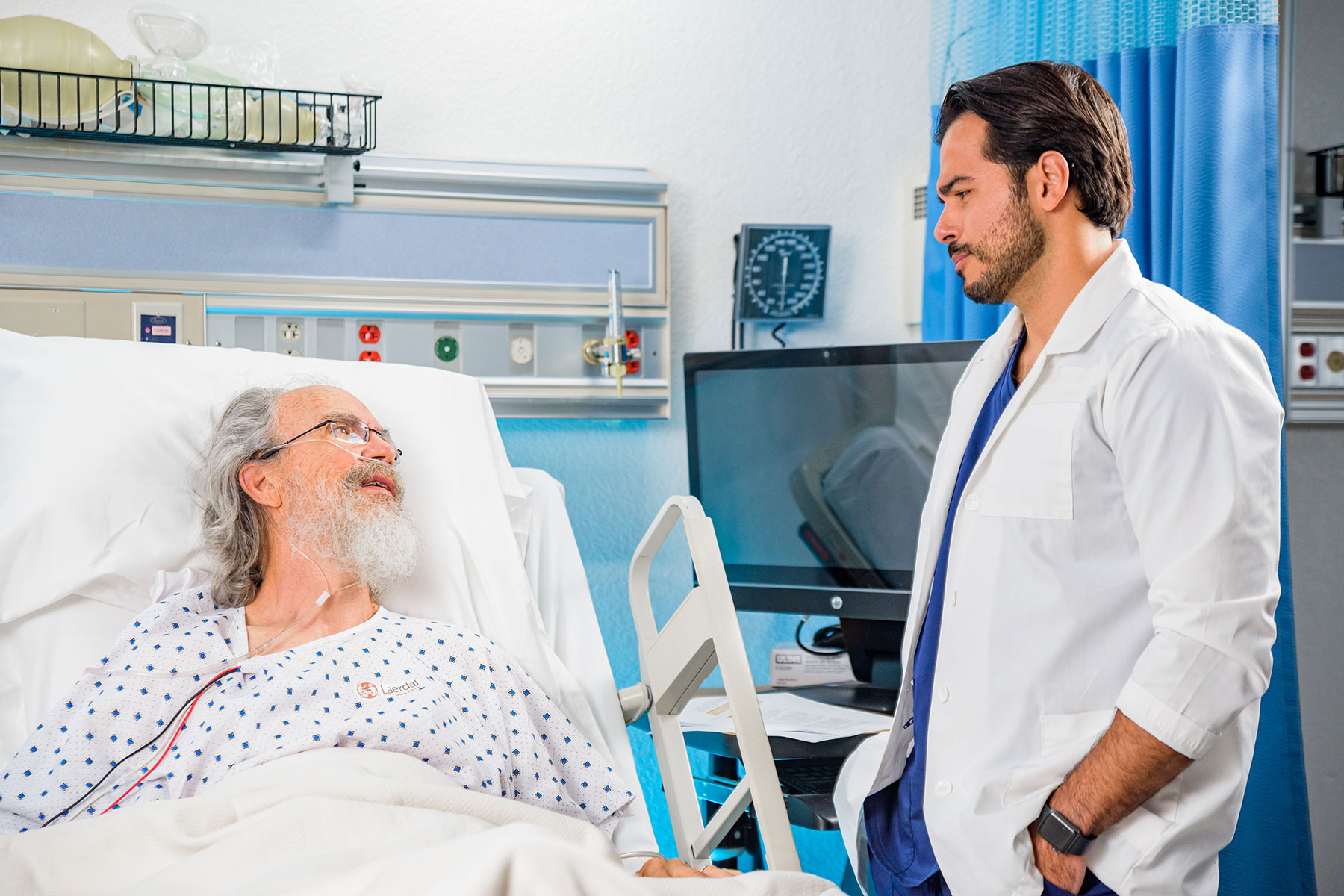
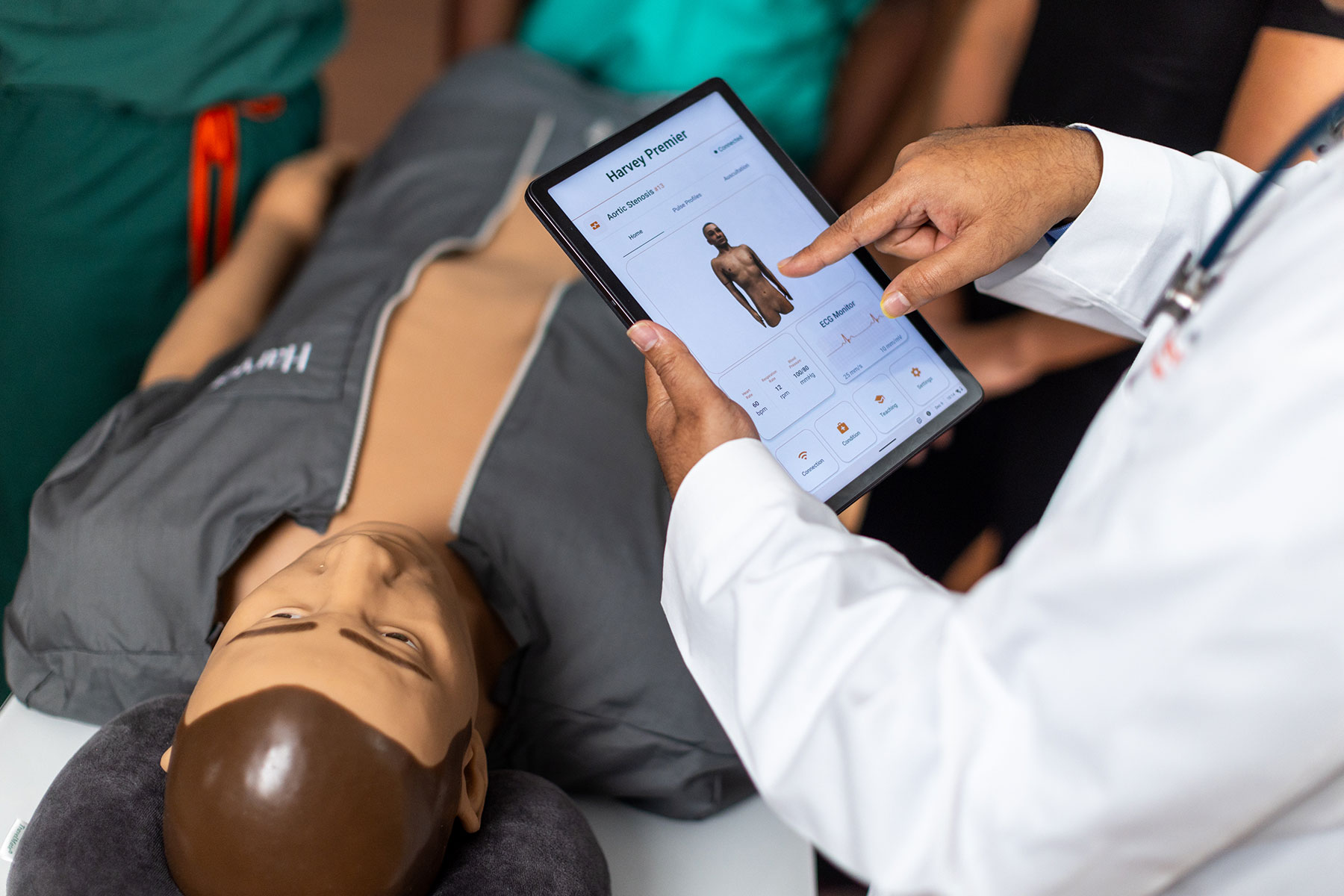
The Role of Simulation in Supporting CBME
Simulation is an essential component of medical school training programs. It serves the dual role of preparing students and evaluating their clinical readiness. It is particularly useful for assessing EPAs that are challenging to consistently observe in clinical settings.
By aligning simulation exercises with EPAs and intended learning outcomes, simulation provides insight into a learner's performance. This helps to shed light on their development towards clinical competence and offers valuable feedback to both educators and students on their progress.