Laerdal Medical Resuscitation Quality Improvement (RQI) Program
3:49
The Resuscitation Quality Improvement (RQI) programs help organisations meet BLS quality and compliance goals utilising RCUK-aligned training, delivered at the point of care.
Healthcare staff shortages, exacerbated by the COVID pandemic, have put pressure on healthcare systems around the world. Meanwhile, scheduling of traditional BLS trainings and tracking compliance have become an even greater challenge with increased staff turnover, strike actions and healthcare providers pressed for time. The result: healthcare organisations are struggling with staff compliance for BLS training.
The Resuscitation Quality Improvement (RQI) programs allow healthcare professionals to obtain BLS credentials and improve their CPR competence through an automated education solution that is delivered in brief sessions at the workplace. Aligned with RCUK guidelines, RQI programs offer self-directed hands-on skills practice and cognitive learning using a low-dose, high-frequency model.
The convenience of obtaining BLS credentials in short sessions at the workplace allows healthcare professionals to focus on what’s important – delivering quality care to every patient, every time.

Automated BLS training
RCUK-aligned, self-directed training is conducted continuously in short sessions at the point of care

True Adaptive eLearning
An innovative algorithm adapts the program entry assignment to the provider’s level of expertise

Hands-on skills training with feedback
Low-dose, high-frequency skills sessions prevent skill decay and feature audiovisual feedback

Measure and improve
RQI Analytics provides insights and trends for compliance and performance over time
RQI verified CPR competence is the higher standard of care, demonstrated to improve clinical care delivery and to increase survival from sudden cardiac arrest.
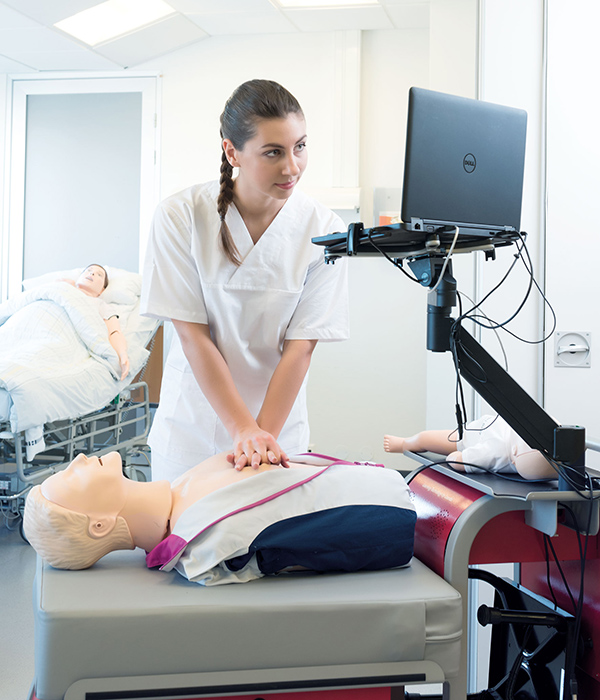
Verified & confident
High-quality CPR
RQI helps ensure your staff has the confidence and competence to perform high-quality CPR when it matters the most.
Low-dose, high-frequency
Frequent but short refresher training sessions make it easier to fit training into your schedule while preventing skills decay.
Objective skills feedback
Standardised skills training is completed on a Simulation Station featuring real-time, audiovisual directive feedback for high-quality CPR skills.

Effective and convenient
True Adaptive Learning
Within the program entry assignment, an innovative algorithm adapts education to each learner’s level of expertise to deliver the most efficient learning path.
Anytime, anywhere, on any device
Featuring responsive design, the eLearning portion can be accessed online anytime, anywhere on a variety of devices.
*Program options without cognitive eLearning available. Inquire for more information.
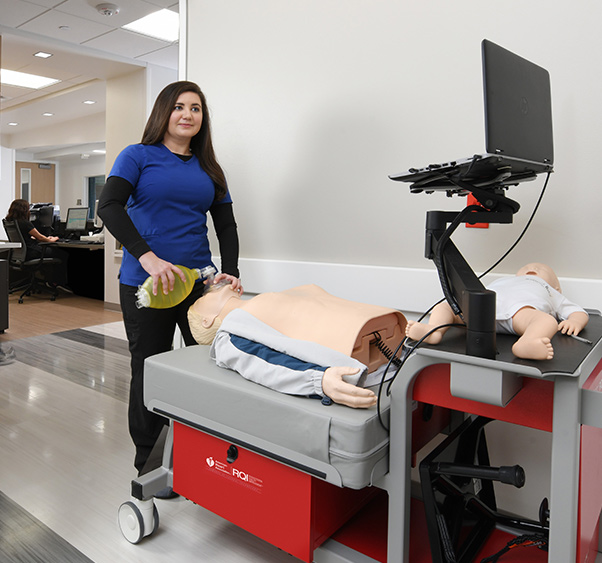
The ROI of RQI
Short training sessions at your convenience
No more all-day-every-two-year-training-classes at an inconvenient location with costly travel. Allow your healthcare providers to conduct 10-minute training sessions, on their floor of the hospital, when it suits them.
Reduced investments and maintenance
The RQI subscription model reduces capital investments, lowers future maintenance costs, and provides support on anything from equipment to software.
Instructor Less Training
Deliver your BLS training whilst adhering to social distancing and free up your time to focus on other areas of resusciatation training.
Low-dose, high-frequency training is the foundation of the Resuscitation Quality Improvement (RQI) programs that measure and verify competence, to help healthcare providers retain life-saving skills.
Learn how the RQI program can help improve resuscitation quality at your hospital.
Find blog posts, how-to's, and evidence library:
"When we started the RQI program only 25% of our staff were able to perform chest compressions and ventilations at the required rate. Now we have more than 90% of staff exceeding the standard."
Matt Johnson, Cabrini Health, Australia
“BLS/PBLS training compliance has greatly increased since adopting RQI and more importantly, compliance can now be tracked accurately. Significant improvement in quality of basic CPR skills has been recognised through RQI feedback. In turn, this has been observed directly in ILS/PILS courses as candidates routinely perform good quality CPR, with little need for correction or intervention required from the instructor.”
Olly Hockin, Spire Healthcare, United Kingdom
1. Kardong-Edgren et al., Baseline Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Skill Performance of Nursing Students is Improved After One Resuscitation Quality Improvement Skill Refresher. Journal for Nurses in Professional Development. 2020; 36(2): 57-62
2. Klacman, A. Barnes, D., & Wang, J. The Effects of a Novel Quarterly Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Training Program on Hospital Basic Life Support Providers’ Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Skill Performance. Journal for Nurses in Professional Development. 2021
3. Dudzik et al., Implementation of a Low-Dose, High-Frequency Cardiac Resuscitation Quality Improvement Program in a Community Hospital. The Joint Commission Journal on Quality and Patient Safety. 2019; 000: 1-9
4. Donoghue, A. et al. Longitudinal effect of high frequency training on CPR performance during simulated and actual pediatric cardiac arrest. Resuscitation Plus. 2021
5. Panchal et al. Low Dose-High Frequency, Case Based Psychomotor CPR Training Improves Compression Fraction For Patients With In-Hospital Cardiac Arrest. European Resuscitation Council. 2020; 146: P26-P31