Improving Patient Care
Simulation-based Education
Globally, the World Health Organization estimates that medical errors result in 2.4 million deaths, every year. Harm from medical care poses a substantial burden in terms of morbidity and mortality on people around the world. It is our vision that no one should die or be disabled unnecessarily during birth or from sudden illness, trauma, or medical errors.
Why improve patient safety?

There is a 1 in 300 chance of a patient being harmed in a hospital.

1 in 4 patients are harmed while receiving primary and ambulatory healthcare.
![]()
Healthcare-associated infections occur in 14 out of every 100 patients.

More than 40 million adverse events occur to patients during hospitalization.
Getting the opportunity to practice
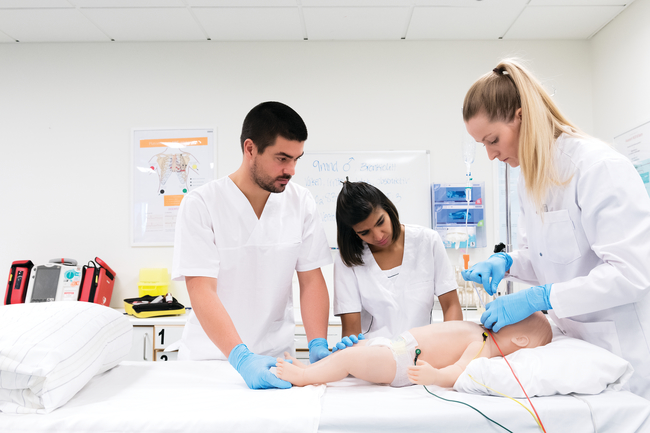
One of the biggest challenges for improving patient safety is the opportunity to practice. Clinical placement opportunities, especially within nurse education, are becoming increasingly limited as the demand for healthcare workers increases due to aging populations.
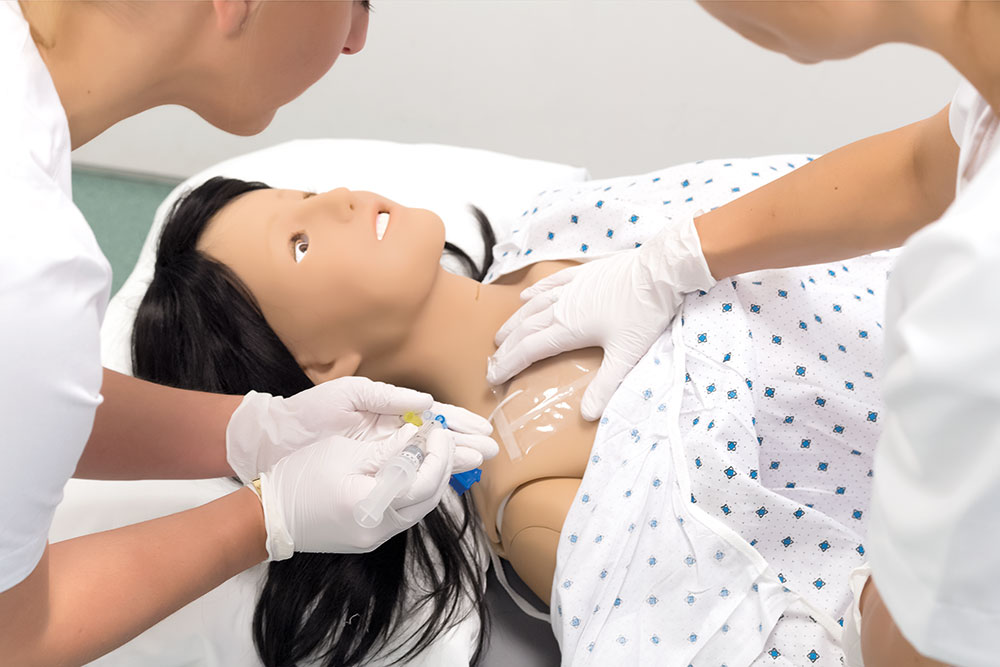
The opportunity for practice is essential, and simulation provides this opportunity without putting patients at risk. Simulation-based training allows students, physicians, nurses, and other healthcare providers to integrate cognitive learning with hands-on skills practice without risk to patients.

Reducing medical errors and improving patient safety are essential elements of patient care, but not the only ones. Providing optimal patient care also includes uncovering latent safety threats, facilitating teamwork and communication, and ensuring professional competency is not only maintained, but improved.
Simulationsbasierte Ausbildung
Die Methodologie der simulationsbasierten Ausbildung ist im Gesundheitswesen mittlerweile weithin als leistungsstarke Maßnahme anerkannt, um klinisches Wissen zu verstärken, die Teamkommunikation zu verbessern und Skills zur Entscheidungsfindung zu lehren. Simulation ist eine Ausbildungsmethode, keine Technologie. Simulation ist nicht nur zur Vermittlung klinischer Skills geeignet, sondern dient auch dem Teamwork und der Kommunikation. Außerdem lässt sich damit das Training standardisieren, und evidenzbasierte Richtlinien und spezifische Ziele können leichter eingehalten bzw. erreicht werden. Mittlerweile geht es weniger darum, was Simulation erreichen kann, sondern die Frage lautet vielmehr, wie man Simulation am besten zur Verbesserung der Patientenfürsorge einsetzt.
Funktioniert Simulation?
Die medizinische Ausbildung verfolgt traditionell den Ansatz „zusehen, selber machen”. In diesem Kontext konzentriert das Lehren sich auf die Weitergabe von Wissen. Beim simulationsbasierten Training erwacht dieses Wissen zum Leben – in einer Umgebung, die reale klinische Situationen und realistische Erfahrungen nachahmen soll, bei denen Klinikkräfte sowohl ihre individuellen Skills als auch die im Team schulen können, ohne ein Risiko für reale Patienten darzustellen.
Wie kann Ihnen Laerdal weiterhelfen?
Key research